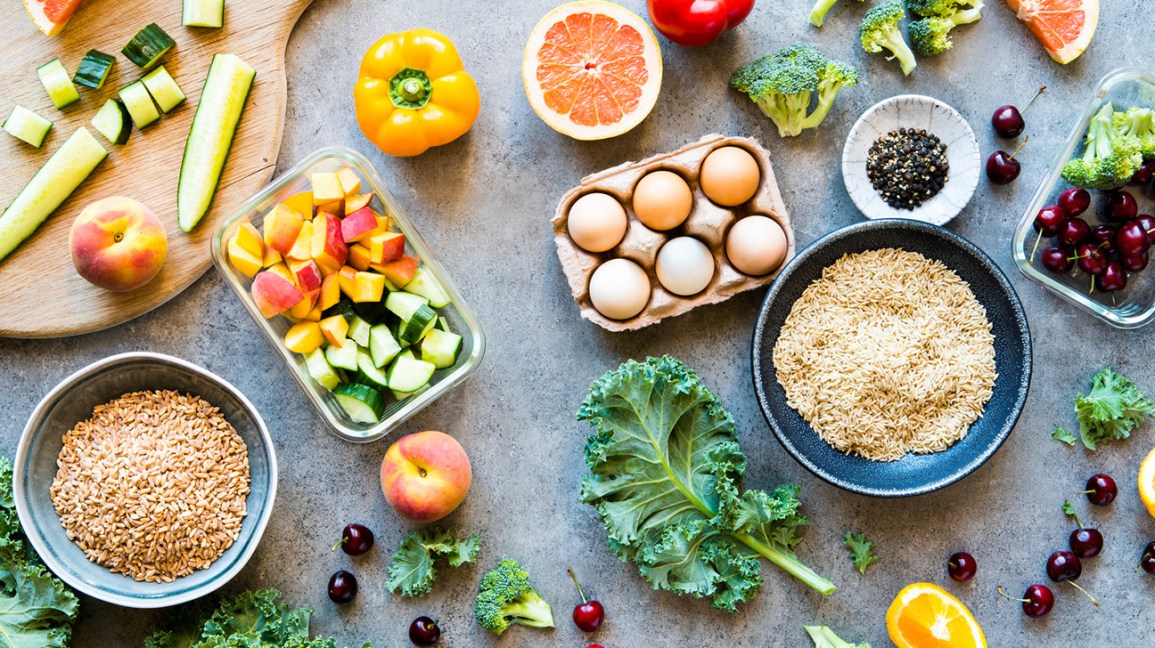
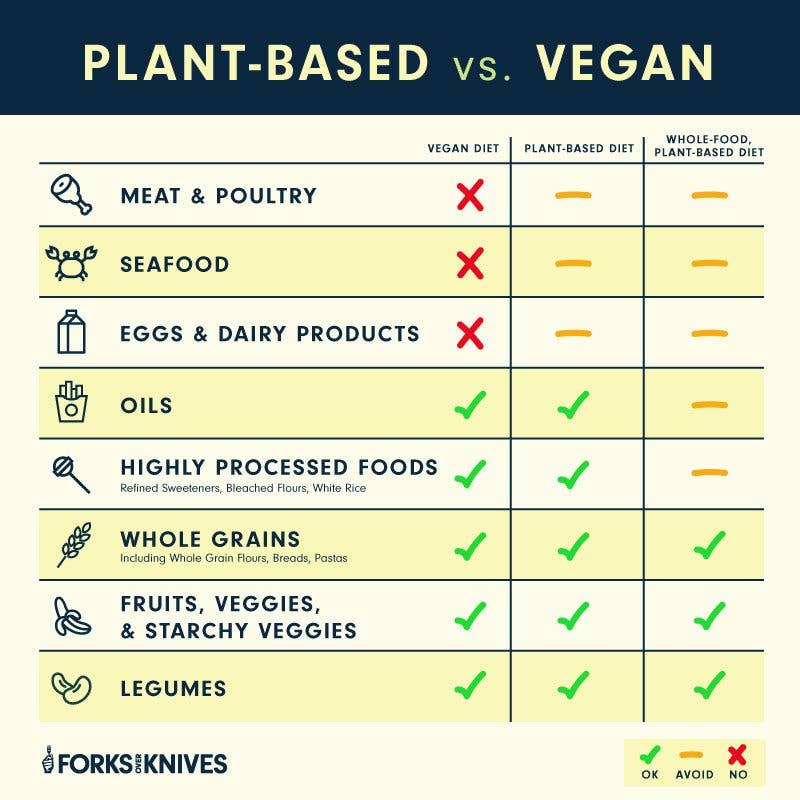
A Whole Food Plant-Based Diet focuses on consuming whole, unprocessed plant foods. It excludes animal products and processed foods.
A Whole Food Plant-Based Diet emphasizes natural, nutrient-dense foods. Fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds form the core of this diet. It promotes better health by reducing the intake of processed and animal-derived foods. Studies show it can lower the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Adopting this diet supports weight loss and boosts energy levels. It also benefits the environment by reducing the carbon footprint. Transitioning to a Whole Food Plant-Based Diet can seem challenging but offers significant health and ecological advantages. Start with small changes and gradually increase plant-based food intake.
Credit: www.forksoverknives.com
The Essence Of A Whole Food Plant Based Diet
A Whole Food Plant Based Diet focuses on consuming natural, unprocessed plant foods. This diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. It avoids processed foods, refined sugars, and animal products. The goal is to eat foods in their natural state. This promotes better health and well-being.
Key Components
- Fruits and Vegetables: These should make up a large portion of your diet. They provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Whole Grains: Choose whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats. They are rich in nutrients and help maintain energy levels.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and peas are excellent sources of protein and fiber. They also contain important vitamins and minerals.
- Nuts and Seeds: These are packed with healthy fats, protein, and various nutrients. Include a variety of nuts and seeds in your meals.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Stay away from foods that are refined or contain added sugars and unhealthy fats.
Health Benefits
A Whole Food Plant Based Diet offers numerous health benefits. These include weight management, reduced risk of chronic diseases, and improved digestion.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Weight Management | Plant-based foods are low in calories and high in nutrients, aiding in weight control. |
| Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases | This diet helps lower the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. |
| Improved Digestion | High fiber content in plant foods promotes better digestion and gut health. |

Credit: www.forksoverknives.com
Transitioning To Whole Food Plant-based Eating
Transitioning to a Whole Food Plant-Based (WFPB) diet can seem overwhelming. This change promises better health and a lighter environmental footprint. With proper guidance, it can be an enjoyable journey.
Getting Started
Start your transition gradually. Introduce more fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes into your meals. Replace one animal-based meal with a plant-based option each day.
Stock up on plant-based staples. Fill your pantry with items like beans, lentils, quinoa, and oats. Fresh fruits and vegetables should always be on your shopping list.
Experiment with new recipes. Try different plant-based recipes to find what you enjoy. Cooking at home allows you to control the ingredients and ensure they are whole and unprocessed.
Meal prep for success. Preparing meals in advance can save time and reduce the temptation to reach for less healthy options. Use weekends to batch-cook grains, beans, and roasted vegetables.
Overcoming Challenges
Cravings for animal products can be tough. Satisfy your taste buds with plant-based versions of your favorite dishes. Try veggie burgers, tofu scrambles, or dairy-free cheese.
Eating out can be tricky. Research restaurants that offer plant-based options or ask for customized meals. Many places are now accommodating dietary preferences.
Nutrient concerns are common. Ensure you get enough protein, iron, and B12. Include a variety of legumes, nuts, seeds, and fortified foods in your diet.
Stay motivated. Surround yourself with supportive communities, either online or in person. Share your journey and learn from others who are on the same path.
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Cravings for animal products | Try plant-based versions of favorite dishes |
| Eating out | Research restaurants or customize meals |
| Nutrient concerns | Include a variety of legumes, nuts, seeds, and fortified foods |
| Staying motivated | Join supportive communities |
Nutritional Foundations Of Plant-based Diets
A Whole Food Plant-Based (WFPB) diet focuses on foods derived from plants, such as vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. This diet excludes or minimizes animal products and processed foods. Understanding the nutritional foundations of plant-based diets helps you make informed choices and ensures you get all essential nutrients.
Essential Nutrients
Plant-based diets are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants. These nutrients support overall health and well-being. Here are some essential nutrients to focus on:
- Protein: Sources include beans, lentils, chickpeas, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa.
- Iron: Found in spinach, lentils, chickpeas, pumpkin seeds, and fortified cereals.
- Calcium: Available in broccoli, kale, almonds, and fortified plant milks.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Sourced from flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and hemp seeds.
- Vitamin B12: Typically found in fortified plant milks and nutritional yeast.
- Vitamin D: Obtain from sunlight exposure and fortified foods like plant milks and cereals.
Balancing Your Meals
Balancing your meals ensures you get a variety of nutrients. Here are some tips:
- Include a variety of colors: Different colors represent different nutrients. Aim for a colorful plate.
- Combine protein sources: Mix legumes with whole grains for complete protein.
- Incorporate healthy fats: Add avocados, nuts, and seeds to your meals.
- Focus on whole foods: Choose unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water and include water-rich foods like cucumbers and melons.
Here’s a simple example of a balanced meal:
| Food Group | Example |
|---|---|
| Protein | Quinoa and black beans |
| Vegetables | Steamed broccoli and carrots |
| Healthy Fats | Avocado slices |
| Whole Grains | Brown rice |
| Fruit | Mixed berries |
Exploring The Variety In Plant-based Cuisine
The whole food plant-based diet is not just about eating fruits and vegetables. It’s a journey of discovering diverse flavors and endless possibilities. From creative cooking ideas to global inspirations, plant-based cuisine offers something for everyone.
Creative Cooking Ideas
Experimenting with plant-based ingredients can be fun and rewarding. You can create delicious dishes with simple vegetables, grains, and legumes.
Here are some creative cooking ideas to inspire you:
- Stuffed Bell Peppers: Fill bell peppers with quinoa, black beans, corn, and spices.
- Zucchini Noodles: Use a spiralizer to make noodles from zucchini. Top with tomato sauce and fresh basil.
- Cauliflower Pizza Crust: Blend cauliflower into a crust. Add your favorite plant-based toppings.
These ideas show that eating plant-based can be both exciting and delicious.
Global Inspirations
Plant-based cuisine is rich with global flavors. Different cultures offer unique dishes that are both nutritious and tasty.
Here are some global plant-based dishes to try:
| Dish | Country | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Chana Masala | India | Spicy chickpea curry with tomatoes and onions. |
| Falafel | Middle East | Deep-fried balls made from ground chickpeas. |
| Ratatouille | France | Stewed vegetable dish with tomatoes, zucchini, and eggplant. |
These dishes illustrate the diverse flavors of plant-based cuisine from around the world.
Embrace the variety of a whole food plant-based diet. Enjoy the journey of exploring new and exciting flavors.
Impact On Physical Health And Vitality
A Whole Food Plant Based (WFPB) Diet can significantly impact your physical health and vitality. This diet focuses on consuming whole, unprocessed plant foods. This includes fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and seeds. The benefits are vast and well-documented.
Weight Management
One of the key benefits of a WFPB diet is effective weight management. Whole plant foods are naturally lower in calories and higher in nutrients. This makes it easier to maintain a healthy weight.
Foods rich in fiber help you feel full longer. This reduces the likelihood of overeating. A study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition showed that participants on a WFPB diet lost more weight than those on other diets.
| Food Type | Calories per 100g | Fiber Content |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits | 50-90 | 2-7g |
| Vegetables | 20-50 | 2-4g |
| Whole Grains | 100-350 | 6-15g |
Chronic Disease Prevention
A WFPB diet also plays a crucial role in preventing chronic diseases. Studies show that plant-based diets can reduce the risk of heart disease. They also lower the risk of type 2 diabetes and certain cancers.
- Heart Disease: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables can lower blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Whole grains and legumes help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Cancer: Antioxidants in plants help protect cells from damage.
The antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals found in plant foods are essential. They help the body fight off disease. A study in The Lancet found that people who eat more plant foods live longer and healthier lives.
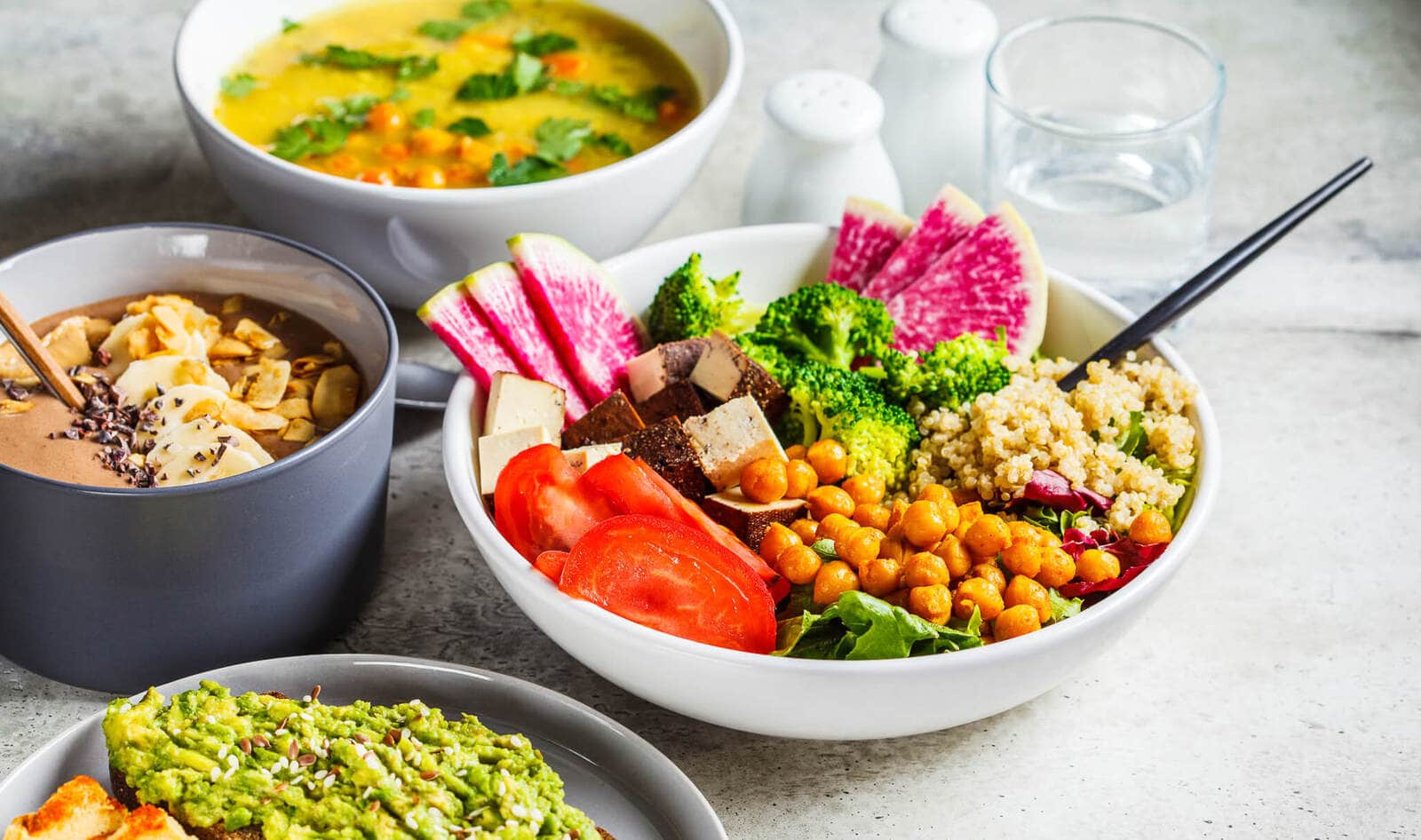

Credit: vegnews.com
Mental And Emotional Benefits
Eating a whole food plant-based diet can do wonders for your mental and emotional health. This diet provides essential nutrients that support brain function and emotional well-being. Let’s explore some of the key benefits.
Enhanced Mood
A whole food plant-based diet can significantly boost your mood. Foods rich in complex carbohydrates, like whole grains, provide a steady release of energy. This helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, which can help prevent mood swings.
Plant-based foods are also high in antioxidants. These antioxidants fight inflammation and oxidative stress, which are linked to mood disorders. Eating more fruits and vegetables can help you feel more positive and energetic.
Moreover, this diet is rich in vitamins and minerals such as magnesium, folate, and vitamin B6. These nutrients are essential for the production of serotonin, the “feel-good” hormone. Higher levels of serotonin can make you feel happier and more relaxed.
Cognitive Improvements
A whole food plant-based diet can also improve your cognitive functions. Foods like nuts, seeds, and leafy greens are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These fats are crucial for brain health and can enhance memory and focus.
Additionally, this diet promotes better gut health, which is directly linked to brain health. A healthy gut microbiome can improve mental clarity and cognitive function. Eating a variety of plant-based foods can help maintain a balanced gut flora.
Studies have shown that a diet rich in antioxidants and polyphenols can protect against age-related cognitive decline. Consuming berries, green tea, and dark chocolate can keep your brain sharp as you age.
| Benefit | Food Source |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Mood | Whole grains, fruits, vegetables |
| Cognitive Improvements | Nuts, seeds, leafy greens |
Sustainability And Ethical Considerations
A Whole Food Plant Based Diet is not just healthy; it is also good for the planet and animals. Choosing this diet can make a big difference in our world. Let’s explore the sustainability and ethical considerations of this diet.
Environmental Impact
Eating plant-based foods helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Animal agriculture is a major source of these harmful gases. Switching to a plant-based diet can cut your carbon footprint significantly.
Growing plants for food uses less water than raising animals. Producing plant-based foods also requires less land. This means more forests and natural habitats can be saved.
Here is a simple comparison of resources used:
| Resource | Animal-Based Diet | Plant-Based Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Water | High Usage | Low Usage |
| Land | More Land Needed | Less Land Needed |
| Greenhouse Gases | High Emissions | Low Emissions |
Animal Welfare
Choosing a plant-based diet means fewer animals are raised and killed for food. Animals on factory farms often live in poor conditions. They do not have space to move or live naturally.
Eating plant-based foods reduces the demand for meat, dairy, and eggs. This means fewer animals will suffer. Supporting plant-based options helps promote kinder treatment for animals.
Here are some benefits for animals:
- Less suffering in factory farms
- More natural habitats for wild animals
- Better health for farm animals
Adopting a Whole Food Plant Based Diet is a powerful choice. It helps the environment and supports animal welfare. Every meal can make a difference.
Real-life Success Stories
The Whole Food Plant-Based Diet has transformed countless lives. People find better health and happiness. Real-life success stories inspire and motivate many to make the switch.
Personal Transformations
Many individuals have experienced incredible personal transformations. These stories highlight the power of a Whole Food Plant-Based Diet.
| Name | Health Issue | Transformation |
|---|---|---|
| John | Obesity | Lost 50 lbs in 6 months |
| Mary | High Blood Pressure | Normalized blood pressure in 3 months |
| Sarah | Diabetes | Reduced medication by 75% |
John struggled with obesity for years. After switching to a Whole Food Plant-Based Diet, he lost 50 lbs in just 6 months. His energy levels skyrocketed.
Mary had high blood pressure. Within 3 months of adopting the diet, her blood pressure normalized. She felt more vibrant and active.
Sarah managed her diabetes with medication. After following the diet, she reduced her medication by 75%. Her blood sugar levels are now stable.
Community Movements
Communities worldwide embrace the Whole Food Plant-Based Diet. They see collective benefits and shared health improvements.
- Plant-Powered Community: A group of neighbors started a plant-based meal club. They share recipes and support each other.
- School Initiatives: Some schools introduce plant-based meals in cafeterias. Students love the tasty and healthy options.
- Workplace Wellness: Companies promote plant-based diets through wellness programs. Employees report better health and productivity.
The Plant-Powered Community started a plant-based meal club. Neighbors meet weekly to share recipes. They support each other’s health goals.
In some schools, plant-based meals are now available in cafeterias. Students enjoy these tasty and healthy options.
Many companies promote plant-based diets through wellness programs. Employees report better health and increased productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Do You Eat On A Whole Food Plant-based Diet?
A whole food plant-based diet includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Avoid processed foods and animal products.
What Is The Downside Of A Plant-based Diet?
A plant-based diet may lack essential nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids. Some people find it challenging to get enough protein. It can also be more time-consuming to plan balanced meals.
Can I Eat Eggs On A Plant-based Diet?
No, a plant-based diet excludes animal products, including eggs. Focus on fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and seeds.
What Are The Rules For Whole Food Plant-based Diet?
A whole food plant-based diet focuses on consuming unprocessed plant foods. Eat fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Avoid refined sugars, oils, and processed foods. Prioritize organic and non-GMO produce. Drink plenty of water and limit salt intake.
Conclusion
Adopting a whole food plant-based diet can transform your health. It promotes weight loss and boosts energy levels. This lifestyle reduces the risk of chronic diseases. Start enjoying vibrant, nutrient-rich meals today. Embrace a healthier, happier you with a plant-based diet.
Your body will thank you for it.